What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) happens when blood does not flow to part of the heart. Learn what causes a heart attack, what you can do to recognize a heart attack, and help yourself recover.
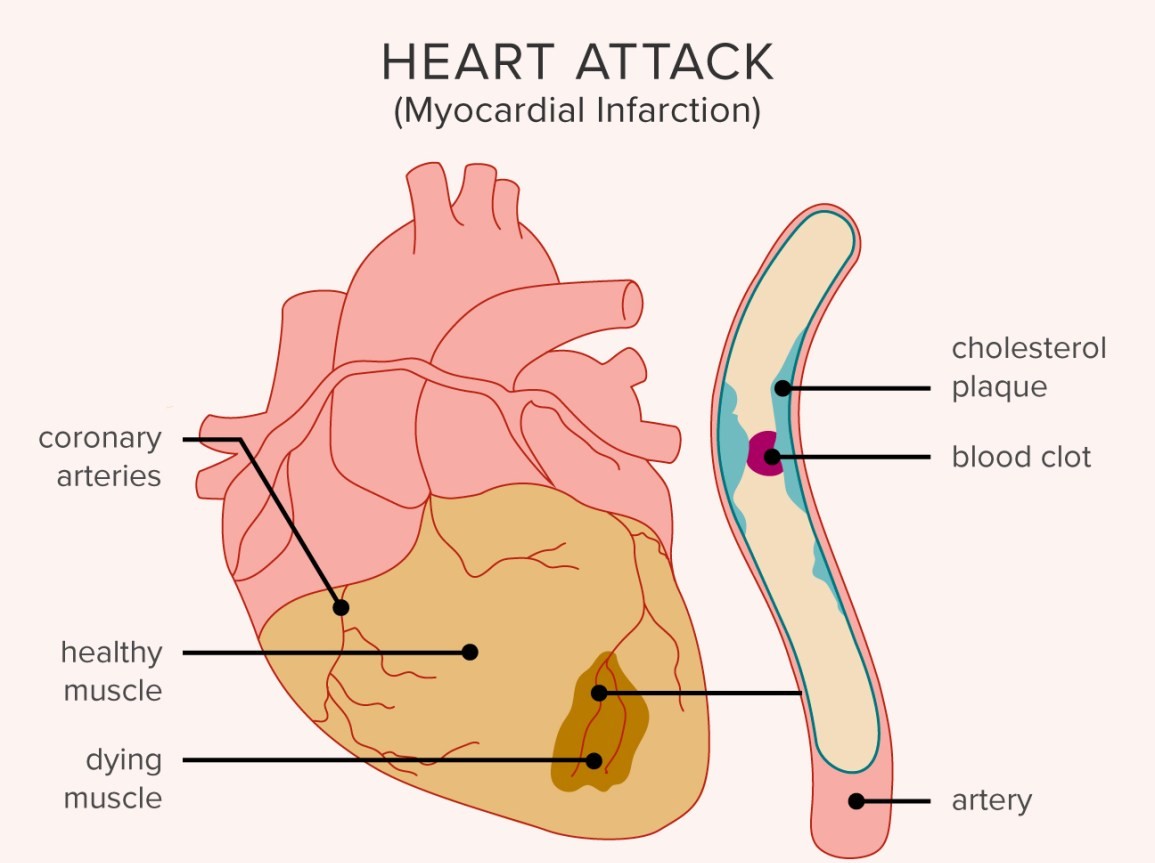
A heart attack happens when the coronary arteries which supplies blood to your heart, becomes blocked.
- The most common sign of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort that can spread to the arms, neck, chin, or back.
- The chest discomfort or pain may last a few minutes or come and go.
- A heart attack requires urgent treatment to get blood back to the heart.
- If you think, you or someone else might be having a heart attack, immediately call doctor.
A heart attack occurs when blood does not flow to part of the heart muscle. If the blood flow does not return quickly, it can lead to permanent heart damage.
If you think someone has heart attack, ask for an ambulance.
The heart is a muscular pump that’s a larger than your fist. It is one of the most important muscles because it pumps blood throughout the body through the arteries.
The blood normally carries all the oxygen it needs for every cell in the body. The heart sends oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart and then to other organs of the body.
What causes a heart attack?
Coronary artery disease (also called atherosclerosis) is a common cause of heart attack. This is when fat and other substances build up in the artery. These diseases are called atheroma or plaque. If one of the plaques crack, a blood clot will form which can block the artery and cause a heart attack.
The most common cause of heart attack is coronary heart disease. It happens when the coronary artery which supplies blood to your heart, narrows because of a build-up of plaque. Plaque is made up of oil, cholesterol, and other substances. Narrowed artery reduce blood flow to the heart muscle.
When the heart stops, plaque from the artery wall breaks away (ruptures) and can form a clot. This can block blood flow in the artery and cause damage of the heart muscle.
While there is a lot we don’t understand about the causes of heart attack, people with a family history of heart disease or stroke are more likely to have a heart attack themselves.
If you are under 50, having a heart attack immediately puts your family at a higher risk for heart disease.
Also Read: What is a Normal Heart Rate?
Symptoms of heart attack
Warning signs of heart attack may include heaviness, pressure, a feeling of tightness, discomfort or pain in the chest, shoulders, jaw, arms, neck or back, sometimes accompanied sweating, shortness of breath, nausea, fatigue or dizziness.
It is possible to have a ‘silent’ heart attack, where you won’t feel any pain, or where the only warning sign may be an poor digestion. This is more common in women or people with diabetes. This is a treatment called asymptomatic ischemia (lack of oxygen) of the heart muscle.
Heart attack symptoms in women
Women can have different heart attack symptoms than men. This is probably because women are more likely to have blockages in the large coronary arteries as well as in the small blood vessels that come out of the arteries. This is called microvascular coronary artery disease.
Symptoms of a heart attack can be subtle in women, so knowing what to look for is important.
Difference between heart attack and cardiac arrest?
Heart attack
A heart attack occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart becomes blocked, which stops blood flow and reduces the flow of oxygen to the heart.
People who have a heart attack often lose consciousness and may complain of chest discomfort or pain or other symptoms.
Cardiac arrest
A cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating due to a malfunction in the electrical system.
Patients with cardiac arrest (unable to respond) and shortness of breath. This is because the heart immediately stops and blood cannot enter the brain, heart and lungs.
Cardiac arrest is emergency medical treatment. If the heart does not start right away, the cardiac arrest can cause brain damage and even death. Every second counts. If you notice a heart attack, immediately call. Giving Chest compressions and the use of an external defibrillator (AED) can increase your chances of survival.
Also Read: Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
How can you reduce the risk of having a heart attack?
Knowing your risk for heart disease is the first step in lowering your risk for a heart attack. But a lot of people don’t know they are in the situation. More than two-thirds of Australian adults, or 12 million, have three or more risk factors for heart attack.
The best way to find out your risk for heart attack is to see your GP for a heart health check if you’re over 45 (or 30 for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people).
Lifestyle changes with the help of your doctor can lower your risk.
How is a heart attack diagnosed?
Heart attack is a medical emergency. If you have symptoms of a heart attack, call and request an ambulance. Ambulance is the safest and fastest way to get to the hospital. When paramedics arrive, treatment can begin, saving valuable time and preventing damage to your heart muscle.
When you arrive at the hospital, your doctor will check if you have heart attack. This test also measures the damage to the heart and the best treatment that can be done.
These tests include:
- Blood tests
- Coronary catheterisation (angiogram)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Also Read: Amazing Health Benefits Of Copper In Water
How is a heart attack treated?
A heart attack requires urgent treatment to get blood back to the heart. The faster this happens, the less damage your heart muscles will be. Heart attack treatments can include medication or surgery.